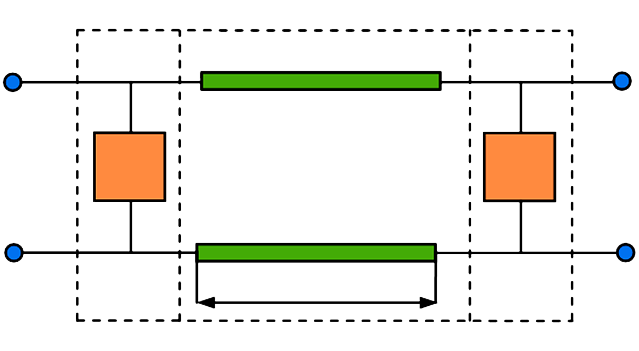
Analytical method of constructive synthesis of compact polarizers with maximally flat phase-frequency characteristic based on two reactive elements in square waveguide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3103/S0735272722090035Keywords:
analytical synthesis, constructive synthesis, maximally flat phase-frequency characteristic, polarizerAbstract
The paper proposes a developed approximate analytical method of constructive synthesis of compact polarizers based on two reactive elements in a square waveguide. The analytical synthesis was carried out under conditions of the absence of reflection and obtaining a required phase shift. As a result, simple formulas have been derived that determine parameters of phase-shifting elements and the electrical distance between them. The constructive synthesis was performed under conditions of the equality of required and real admittances of posts and diaphragms in a square waveguide and their derivatives at the central frequency of the working frequency band. As a result, the real geometrical dimensions of polarizers based on two posts and based on two diaphragms in a square waveguide were determined that provided for maximally flat phase-frequency characteristic. It has been shown that the polarizer based on two posts in a square waveguide can ensure the working frequency band of 4% or 13% while reflecting the electromagnetic energy of less than 1% or 10%, respectively, and differential phase shift Δφ = 90° ± 1°. However, polarizer based on two diaphragms in a square waveguide under the same conditions can ensure the working frequency band of up to 11% or 18%, respectively. The theoretical results were confirmed by experimental data.
References
- S. Piltyay, A. Bulashenko, V. Shuliak, “Development and optimization of microwave guide polarizers using equivalent network method,” J. Electromagn. Waves Appl., vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 682–705, 2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09205071.2021.1980913.
- A. J. Simmons, “A compact broad-band microwave quarter-wave plate,” Proc. IRE, vol. 40, no. 9, pp. 1089–1090, 1952, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JRPROC.1952.273879.
- A. J. Simmons, “Phase shift by periodic loading of waveguide and its application to broad-band circular polarization,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 18–21, 1955, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1955.1124986.
- E. E. Altshuler, “A periodic structure of cylindrical posts in a rectangular waveguide,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 398–402, 1961, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.1961.1125360.
- F. F. Dubrovka, O. M. Kuprii, “Synsesis of microwave phase shifters based on reactive elements in waveguide,” Izv. Vyss. Uchebnykh Zaved. Radioelektronika, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 25–28, 1982.
- Y. Liu, F. Li, X. Li, H. He, “Design and optimization of wide and dual band waveguide polarizer,” in 2008 Global Symposium on Millimeter Waves, 2008, pp. 384–386, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/GSMM.2008.4534654.
- G. Virone, R. Tascone, O. A. Peverini, R. Orta, “Optimum-iris-set concept for waveguide polarizers,” IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett., vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 202–204, 2007, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LMWC.2006.890474.
- G. Virone, R. Tascone, M. Baralis, O. A. Peverini, A. Olivieri, R. Orta, “A novel design tool for waveguide polarizers,” IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 53, no. 3, pp. 888–894, 2005, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2004.842491.
- G. Virone, R. Tascone, O. A. Peverini, G. Addamo, R. Orta, “Combined-phase-shift waveguide polarizer,” IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett., vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 509–511, 2008, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/LMWC.2008.2001005.
- S. Hwang, J. Kim, K. Lee, “Study on design parameters of waveguide polarizer for satellite communication,” in 2012 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, pp. 153–154, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/APCAP.2012.6333202.
- B. Subbarao, V. F. Fusco, “Differential phase polarizer used for RCS control,” in IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society Symposium, 2004., 2004, pp. 4256-4259 Vol.4, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/APS.2004.1330291.
- A. Chittora, S. V. Yadav, “A compact circular waveguide polarizer with higher order mode excitation,” in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), 2020, pp. 1–4, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CONECCT50063.2020.9198499.
- A. Bulashenko, S. Piltyay, O. Bykovskyi, O. Bulashenko, “Synthesis of waveguide diaphragm polarizers using wave matrix approach,” in 2021 IEEE 3rd Ukraine Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (UKRCON), 2021, pp. 111–116, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/UKRCON53503.2021.9575322.
- S. Piltyay, A. Bulashenko, V. Shuliak, O. Bulashenko, “Electromagnetic simulation of new tunable guide polarizers with diaphragms and pins,” Adv. Electromagn., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 24–30, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.7716/aem.v10i3.1737.
- F. F. Dubrovka, A. V. Bulashenko, A. M. Kuprii, S. I. Piltyay, “Analytical and numerical method of constructive synthesis of optimal polarizers based on three irises in square waveguide,” Radioelectron. Commun. Syst., vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 204–215, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3103/S073527272104004X.
- A. V. Bulashenko, S. I. Piltyay, I. V. Demchenko, “Wave matrix technique for waveguide iris polarizers simulation. Numerical results,” J. Nano- Electron. Phys., vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 05023-1-05023–6, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.13(5).05023.
- W. L. Stutzman, Polarization in Electromagnetic Systems, 2nd ed. Artech House, 2018, uri: https://us.artechhouse.com/Polarization-in-Electromagnetic-Systems-Second-Edition-P1945.aspx.
- Y. Herhil, S. Piltyay, A. Bulashenko, O. Bulashenko, “Characteristic impedances of rectangular and circular waveguides for fundamental modes,” in 2021 IEEE 3rd Ukraine Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (UKRCON), 2021, pp. 46–51, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/UKRCON53503.2021.9575359.
- D. M. Pozar, Microwave Engineering, 4th ed. New Jersey: Wiley and Sons, 2011, uri: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Microwave+Engineering%2C+4th+Edition-p-9780470631553.
- J. Helszajn, Microwave Polarizers, Power Dividers, Phase Shifters, Circulators, and Switches. Wiley, 2018, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119490104.